We offer an extensive line of chest tubes for removing both air and fluid from the pleural and pericardial spaces. These products are available in a variety of designs and sizes, including several small-bore configurations, Seldinger and trocar options, and sets and trays to meet specific procedural preferences. View each product’s indications for use, specifications, components, and other resources by clicking the links below.
Pneumothorax catheters
Wayne Pneumothorax Catheter Set and Tray – Seldinger
 Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, iatrogenic, and tension pneumothorax.
Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, iatrogenic, and tension pneumothorax.
Features and benefits
• Seldinger placement facilitates controlled, minimally invasive catheter introduction.
• The set comes with the Cook Chest Drain Valve, which is designed to help remove air from the pleural cavity.
• The enlarged sideports are designed to facilitate the drainage of air.
• The radiopaque catheter material enhances x-ray visualization.
• Pigtail catheters have a comparable efficacy to chest tubes in patients with pneumothorax.*
*Kulvatunyou N, Vijayasekaran A, Hansen A, et al. Two-year experience of using pigtail catheters to treat traumatic pneumothorax: a changing trend. J Trauma. 2011;71(5):1104–1107.
View more details about the Wayne Pneumothorax Catheter Set and Tray – Seldinger.
Wayne Pneumothorax Catheter Set – Trocar
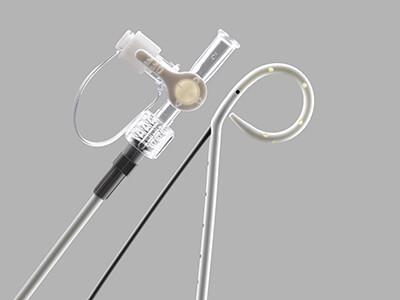 Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, iatrogenic, and tension pneumothorax.
Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, iatrogenic, and tension pneumothorax.
Features and benefits
• The needle obturator comes pre-assembled within the Wayne Pneumothorax Catheter to allow for direct-stick insertion.
• The set comes with the Cook Chest Drain Valve, which is designed to help remove air from the pleural cavity.
• The enlarged sideports are designed to facilitate the drainage of air.
• The radiopaque catheter material enhances x-ray visualization.
• Pigtail catheters have a comparable efficacy to chest tubes in patients with pneumothorax.*
*Kulvatunyou N, Vijayasekaran A, Hansen A, et al. Two-year experience of using pigtail catheters to treat traumatic pneumothorax: a changing trend. J Trauma. 2011;71(5):1104–1107.
View more details about the Wayne Pneumothorax Catheter Set – Trocar.
Cook Emergency Pneumothorax Set
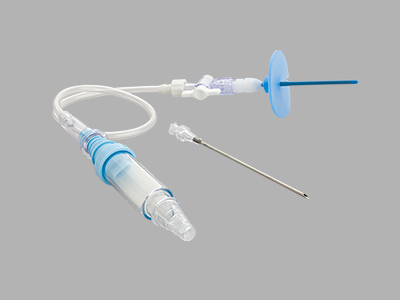 Used for emergency relief and temporary management of suspected tension pneumothorax.
Used for emergency relief and temporary management of suspected tension pneumothorax.
Features and benefits
• The set comes with the Cook Chest Drain Valve, which is designed to help remove air from the pleural cavity.
View more details about the Cook Emergency Pneumothorax Set.
Pneumothorax Set and Tray
 Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, or iatrogenic pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax.
Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, or iatrogenic pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax.
Features and benefits
• The straight catheter is used for trocar placement.
• The radiopaque catheter material enhances x-ray visualization.
• The set and tray come with a vinyl connecting tube and a three-way stopcock.
• The set comes with the Cook Chest Drain Valve, which is designed to help remove air from the pleural cavity.
View more details about the Pneumothorax Set and Tray.
Richli Pneumothorax Catheter Set
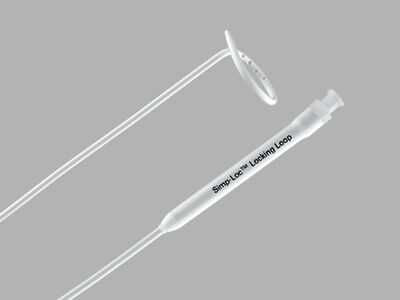 Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, or iatrogenic pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax.
Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, or iatrogenic pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax.
Features and benefits
• Seldinger placement facilitates controlled, minimally invasive catheter introduction.
• The 8.5 Fr catheter is designed for smaller patient anatomies.
• Sideports are positioned within the catheter pigtail and are designed to aid in drainage.
• The set comes with the Cook Chest Drain Valve, which is designed to help remove air from the pleural cavity.
View more details about the Richli Pneumothorax Catheter Set.
Catheter Aspiration Set for Simple Pneumothorax
 Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, or iatrogenic pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax.
Used for the relief of simple, spontaneous, or iatrogenic pneumothorax and tension pneumothorax.
Features and benefits
• Seldinger placement facilitates controlled, minimally invasive catheter introduction.
• The radiopaque catheter material enhances x-ray visualization.
View more details about the Catheter Aspiration Set for Simple Pneumothorax.
Multipurpose catheters
Thal-Quick Chest Tube Set and Tray
 Used for the percutaneous introduction of a chest tube for pleural fluid drainage.
Used for the percutaneous introduction of a chest tube for pleural fluid drainage.
Features and benefits
• Seldinger placement facilitates controlled, minimally invasive catheter introduction.
• The centimeter-marked dilators allow for additional control over the insertion of a chest tube into the pleural space.
• The sideports are positioned at the distal end of the chest tube.
• The clear polyvinylchloride catheter with a radiopaque stripe allows fluid to be seen during the drainage procedure.
• The most proximal side hole is positioned on the radiopaque stripe to aid in confirming catheter positioning via x-ray.
• The double lumen set has an additional lumen available for aspiration or infusion.
• The Thal-Quick Chest Tube Adapter is sold separately.
View more details about the Thal-Quick Chest Tube Set and Tray.
Fuhrman Pleural/Pneumopericardial Drainage Set and Tray

After percutaneous insertion via the Seldinger technique, the pigtail catheter of the Fuhrman Pleural Drainage Set serves as a conduit to drain air or fluid from the pleural space to outside the body.
Features and benefits
• Seldinger placement facilitates controlled, minimally invasive catheter introduction.
• The catheter is available in a variety of sizes, ranging from 5 to 12 Fr, to cater to different patient anatomies.
• Sideports are positioned within the catheter pigtail and are designed to aid in drainage.
• Centimeter markings on the pigtail catheter guide insertion.
• The catheter material has radiopaque properties.
• Pigtail catheters have been shown to have a comparable efficacy to chest tubes in patients with pneumothorax.*
*Kulvatunyou N, Vijayasekaran A, Hansen A, et al. Two-year experience of using pigtail catheters to treat traumatic pneumothorax: a changing trend. J Trauma. 2011;71(5):1104–1107.
View more details about the Fuhrman Pleural/Pneumopericardial Drainage Set and Tray.
Pericardiocentesis catheters
Lock Pericardiocentesis Set and Tray
 Used to remove fluid from the pericardial sac.
Used to remove fluid from the pericardial sac.
Features and benefits
• Seldinger placement facilitates controlled, minimally invasive catheter introduction.
• The 40 cm long catheter is designed to cater to larger patient anatomies.
• The radiopaque catheter material enhances x-ray visualization.
View more details about the Lock Pericardiocentesis Set and Tray.
Peritoneal Lavage Set and Tray

Used to infuse or withdraw rinsing solutions in the peritoneal cavity.
Features and benefits
• Seldinger placement facilitates controlled, minimally invasive catheter introduction.
• The catheter is equipped with 90 sideports.
• The radiopaque catheter material enhances x-ray visualization.
View more details about the Peritoneal Lavage Set and Tray.
Accessories
Simple Pneumothorax Aspiration Accessory Set
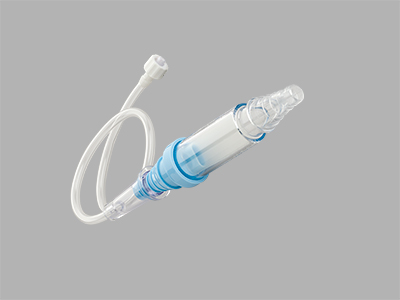 Used in conjunction with a pneumothorax aspiration catheter if incomplete expansion of the lung persists after mechanical aspiration of air.
Used in conjunction with a pneumothorax aspiration catheter if incomplete expansion of the lung persists after mechanical aspiration of air.
Features and benefits
• The set comes with the Cook Chest Drain Valve, which is designed to help remove air from the pleural cavity.
View more details about the Simple Pneumothorax Aspiration Accessory Set.
Multipurpose Plastic Tubing Adapter
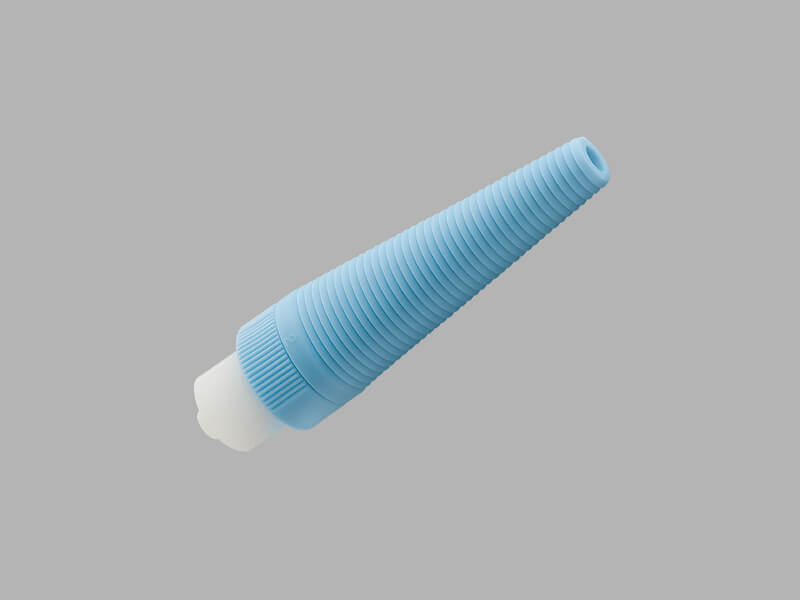 Used for connection to other medical devices such as catheters.
Used for connection to other medical devices such as catheters.
Features and benefits
• The adapter is male Luer lock to a universal taper.
View more details about the Multipurpose Plastic Tubing Adapter.
Vinyl Connecting Tube
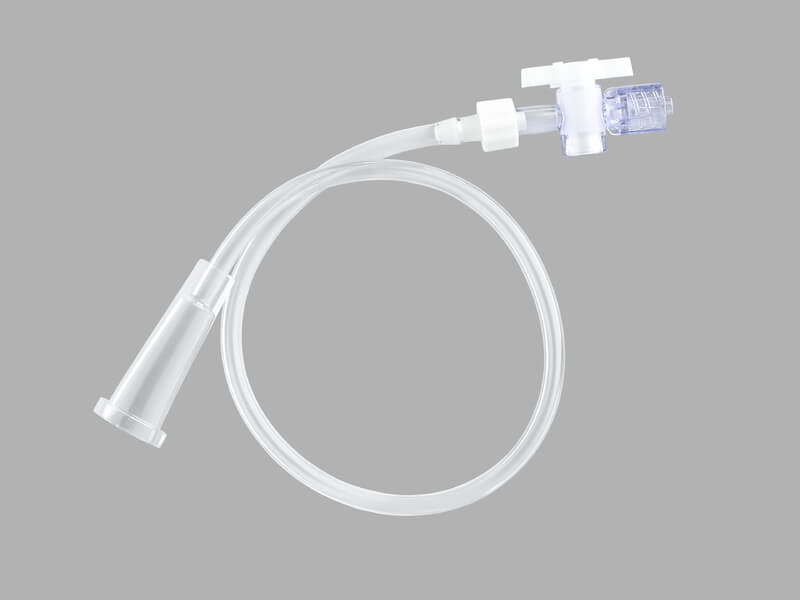 Used for the connection of an external drainage catheter to a drainage pouch.
Used for the connection of an external drainage catheter to a drainage pouch.
View more details about the Vinyl Connecting Tube.
Thal-Quick Chest Tube Adapter
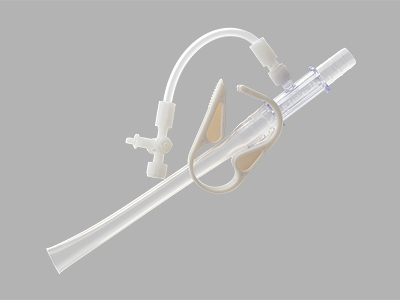 Used to provide separate sampling or an infusion port within Thal-Quick chest tubes.
Used to provide separate sampling or an infusion port within Thal-Quick chest tubes.
Features and benefits
• This accessory is compatible with the Thal-Quick Chest Tube Set and Tray.
View more details about the Thal-Quick Chest Tube Adapter.
Interested in chatting with a Cook Medical representative?
Please submit the required information to connect with your local Cook representative. This form is intended for US-based physicians only. Please see our Privacy Statement for data protection notices relating to our collection and use of your data.
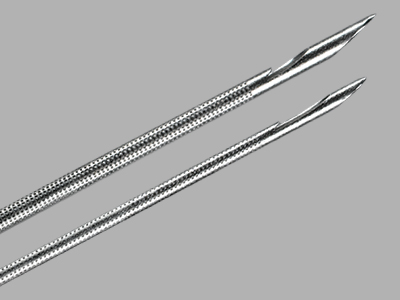 The EchoTip ProCore needle is used with the Olympus® ultrasound endoscope for fine needle biopsy of submucosal and extramural lesions within or adjacent to the tracheobronchial tree or gastrointestinal tract.
The EchoTip ProCore needle is used with the Olympus® ultrasound endoscope for fine needle biopsy of submucosal and extramural lesions within or adjacent to the tracheobronchial tree or gastrointestinal tract.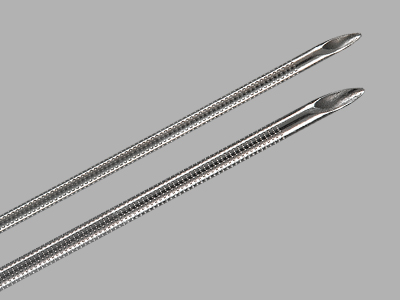 The EchoTip Ultra needle is used with the Olympus ultrasound endoscope for fine needle aspiration of submucosal and extramural lesions within or adjacent to the tracheobronchial tree or gastrointestinal tract.
The EchoTip Ultra needle is used with the Olympus ultrasound endoscope for fine needle aspiration of submucosal and extramural lesions within or adjacent to the tracheobronchial tree or gastrointestinal tract.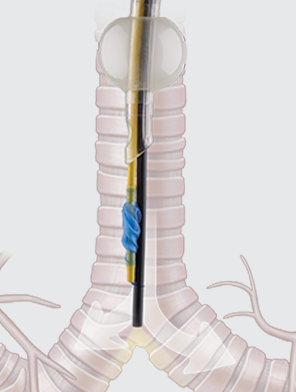 Intended to differentially intubate a patient’s bronchus in order to isolate the left or right lung for procedures that require one-lung ventilation. The product is intended for use by physicians trained and experienced in the use of fiberoptic bronchoscopes and airway anatomy. Standard techniques for use of fiberoptic bronchoscopes and endobronchial blockers should be employed.
Intended to differentially intubate a patient’s bronchus in order to isolate the left or right lung for procedures that require one-lung ventilation. The product is intended for use by physicians trained and experienced in the use of fiberoptic bronchoscopes and airway anatomy. Standard techniques for use of fiberoptic bronchoscopes and endobronchial blockers should be employed. The plenary sessions at the
The plenary sessions at the 