Safe
Zilver PTX is safe and effective for treating PAD
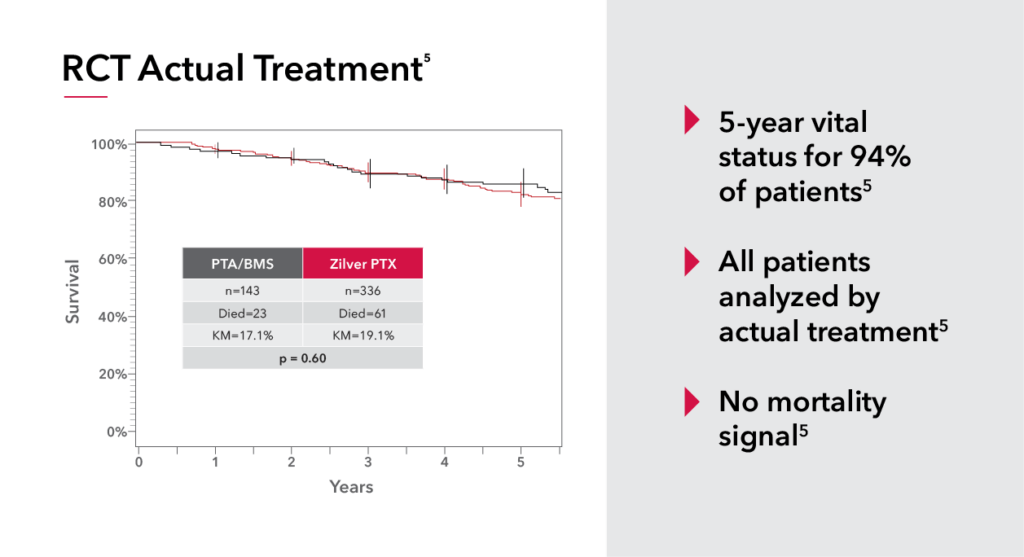
Zilver PTX remains the only SFA DES with a transparent 5-year safety profile.
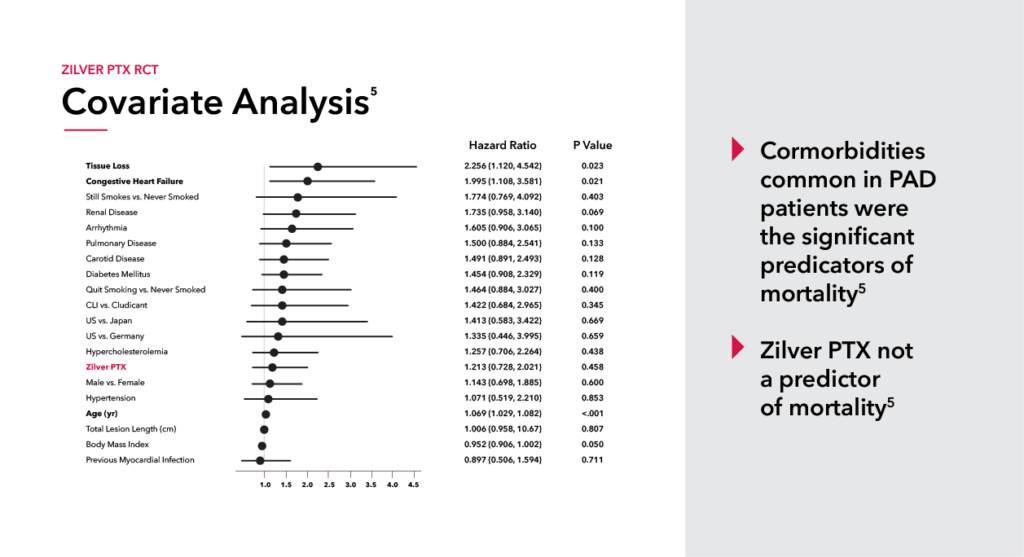
The safety and efficacy of paclitaxel has been rigorously studied by leading physicians and industry partners like Cook. Immediately following the paclitaxel controversy we began thoroughly evaluating our data and in the spirit of transparency released five-year patient-level data from the Zilver PTX randomized control trial. After this rigorous analysis, we concluded there was no increased risk of mortality associated with Zilver PTX.
We were the first and only company to be this transparent with our data.
We have remained dedicated to the safety and efficacy of Zilver PTX and will continue to deliver this proven technology to patients around the world. Zilver PTX has repeatedly achieved long-term success, out to 5-years, and sustained durability1,2,3 with consistently low fracture rates in randomized trials1,4 and remains the only polymer-free drug-eluting stent for the SFA. Our proprietary, polymer-free coating process eliminates the potential risks of permanent polymers. When placing a drug-eluting stent you can feel confident Zilver PTX improve long term outcomes for your patients.
This comprehensive look at paclitaxel has led the FDA to update their stance and to confirm there is no excess mortality risk for paclitaxel-coated devices. This update allows Zilver PTX to be available for all PAD patients instead of only those considered high risk.
You can learn more about the FDA decision and Cook’s stance here. You can also read about Dr. Eric Secemsky’s involvement in researching paclitaxel, industry collaboration, and the importance of drug coated devices to patient safety.
For some, controversies surrounding the use of paclitaxel-coated devices to treat PAD in the SFA have caused concern about patient safety. Transparency is the key to ensuring physicians have access to the safest and most effective technology available for treating PAD in a broad patient population. That’s why we took the unprecedented step of making our 5-year patient-level data fully available for the whole world to see. Our commitment to data transparency led to the creation of our exclusive prediction model.